Sky Charts
Menu Commands
All the commands can be used from the main menu or the tool-bars.
It is possible to move each button group where you want and select which group to display using the View->Tool-bar option from the main menu. You can hide the main menu to free some space on the screen. Use the Space or Esc key to show the menu again.
The tool-bar icons correspond to the main menu functions.
File
![]()
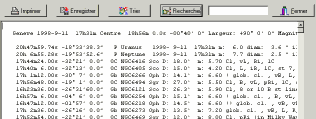
You can click a line in this list to show the detailed
identification window.
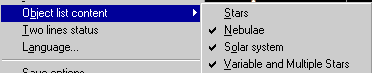
The menu "Preference - Object list content" lets you filter
the object type to show in the list:
- Images from different catalogs.
- Stars from GSC and USNO-A catalogs.
- Update the elements of comets and asteroids.
NOTE - You have to be connected to the Internet before you can
use this function.
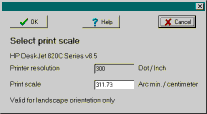
The function projection types allow to use azimuthal projection for the main chart.
It is also possible to type a title and description for the chart, to change the page margin or to not print any legend.
With "Portrait" orientation it is possible to also print the list of the object in the chart to the same sheet of paper. First check with the
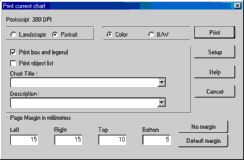
It is possible to use the internal viewer or your default
browser.
![]() Exit the
program
Exit the
program
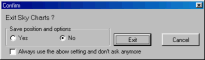
You are asked to select whether you want to save the current
options before you exit. Select Yes if you want to start the next
session at the point you stopped here. If you always respond to
this question in the same manner, you can check the bottom box to
avoid this prompt in the future. The menu Preference allows you
to reactivate this question box.
Publishing
The right mouse button on this icon selects or deselects the
automatic refresh of the current chart after every operation.
![]() Animation.
Animation.
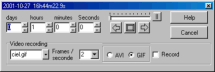
Set the step by days, hours, minutes, seconds then click one of
the arrows to increment or decrement the current time. It is
possible to add a delay by using the cursor or to go step by
step.
The position is constant right ascension and declination in the
case of equatorial coordinates or constant azimuth and altitude
in the case of azimuthal coordinates.
To follow the displacement of a solar system object (planet,
comet or asteroid) select it by a right mouse click and select
"Track ..." from the menu.
For better animation use only necessary options and a minimum
number of catalogs. It is also important to activate the "use memory cache" option.
To record the animation to an AVI or GIF file, indicate the
file name, the playback frame rate, the file format and check the
"Record" box. Be aware this may create a very large AVI file.
View
![]()
This scale lets you quickly select any value between 6' and
360°. To access a smaller field of view down to 2" you can
use the +/- key or the Locate panel.
You can also use a wheelmouse to zoom or the middle button of
a three button mouse + the Ctrl key. These both require a recent
processor (>1000Mhz) to work well.
The following information is displayed:
Magnitudes
Var Variable star
Dbl Double star
b-v Colour index
Gx Galaxy
Oc Open cluster
Gc Globular cluster
Pl Planetary nebula
Neb Bright nebula
N+C Nebula and cluster
Star Cataloged nebula identified as star
Unk Cataloged nebula unidentified
Comet
Asteroid
Planet
Move
![]() Move the chart
in the corresponding direction. You can also use the keyboard
arrows or press the middle button or wheel of the mouse.
Move the chart
in the corresponding direction. You can also use the keyboard
arrows or press the middle button or wheel of the mouse.
Search
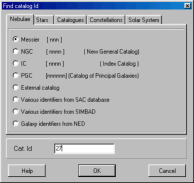
Find an object by name in the following catalogs: Messier, NGC, IC, GCVS, WDS, Boss GC, GSC, SAO, HD, BD+SD, CD, CPD, HR. NOTE - The corresponding catalog or index must be installed. Or use an active external catalog.
Enter the catalog number in the "Cat Id" field. For the GSC, enter region number and star number separated by space. For BD id's enter sign and declination zone number, a space, then star number ( i.e.: +36 2844 ).
To search an object by another catalog identifier like UGC, MCG, PK, ... use the option SAC for the most luminous or the option NED and SIMBAD to access the full catalog via Internet. Please consult the online documentation for specific naming when using these two options.
To find a variable star you can use a name from GCVS like "Y Cas" or "V1357 Cyg" or a suspected variable number like "NSV 1205" or an extragalactic variable name like "SMC V0220" or "N4486 V0002". You can use upper case or lower case for the name. The only exception is "U Her" and "u Her".
Find the planets, comets and asteroids.
The Comets and asteroids list contains only those selected in Catalogs Selection menu.
Find by constellation name, star name (common name, Bayer,
Flamsteed).
For Bayer name enter the Greek letter abbreviation first, then
the constellation abbreviation (i.e.: GAM AND for Gamma
Andromedae). For Flamsteed numbers enter the star number and the
constellation abbreviation.
It is also possible to search for an Uranometria 2000 chart number.
You can do a quick search without opening the main search
window by using this box: ![]()
In this case you must type the catalog name prefix and catalog
number, then press Enter to do the search.
Here are some examples of valid queries: m8, M 8, ngc7331, ic
434, SS cyg, tyc1800 1718, ugc 7517, STF2382, rho oph, 51 peg, pk
29-5.1, mars, ...
Preferences
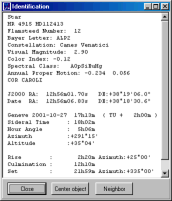
- Default choice for the identification function. Short identification (in the status bar) or long in a popup window. The Alt key swaps this behaviour.
When in Short mode a click to the label opens the detail window.
The "Center" button places this object at the center of the chart. The "Neighbor" button shows a list with all the objects in the vicinity.
- Fonts selection. Use the button on the right to change a
font.
- Program language selection.
Two status line menu: You can use this option to use two lines to display the status information. This permits showing the full information for some objects, but also gives more information about the cursor position.
Moving the cursor:
![]() This shows both equatorial and azimuthal coordinates for any
projection setting.
This shows both equatorial and azimuthal coordinates for any
projection setting.
![]() After you click on two objects this shows the distance between
the two objects, the position angle, and the difference in
position in right ascension and in declination.
After you click on two objects this shows the distance between
the two objects, the position angle, and the difference in
position in right ascension and in declination.
Lines
Click with the right mouse button on this icon to configure the eyepieces :
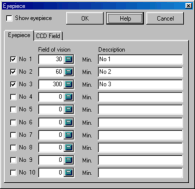
The selection "Eyepiece" lets you choose the appearance of the circle corresponding to the field of view of your eyepiece. It is possible to draw up to ten different eyepieces. Enter the size of the field of view in minutes of arc and the associate label. If you want to know the field of view of your eyepiece, divide the apparent field of view by the magnification. i.e. an eyepiece with a focal length of 20 mm and an apparent field of view of 40° used on a telescope with a focal length of 2000 mm:
Magnification = 2000 / 20 = 100
Viewing field = 40 / 100 = 0.4°
Viewing field = 0.4 * 60 = 24 minutes
The value of 24 is the answer to the question.
More options available only from the main menu:
- Local Horizon : Plot the local horizon from a file containing azimuth and local horizon altitude.
- Ecliptic line.
- Galactic equator line.
- An option to draw a line to connect the position of the planets, comets, asteroids at different dates.
- Milky Way.
- Uranometria 2000 charts boundaries: Plot the chart of this atlas.
Images
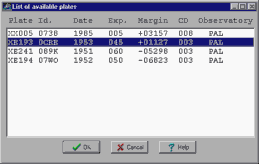
Look at exposure time and margin to help choose the best plate. The margin is positive if the chart is entirely contained in the plate or negative if a truncation occurs at the plate border.
The right mouse button lets you change the blinking speed.
Telescope
![]()
These are the commands that control a telescope from the
program. They are available from the button bar, the menu bar or
with a right click of the mouse.
Menu Telescope - Select Scope Interface: Select the interface type you want to use. Only correctly installed optional plugin are displayed.
The following models are actually supported:
Plugin Encoder: encoder based on Tangent system, Ouranos, NGC-Max, etc...
Plugin Meade: Meade telescope LX200, ETX, LX90, Magellan or compatible models.
Plugin ASCOM: Any telescope supported by the ASCOM platform including most Celestron models.
![]() Open the
interface screen to configure and connect the telescope.
Open the
interface screen to configure and connect the telescope.
![]() Move the chart
center to the current telescope position.
Move the chart
center to the current telescope position.
![]() Permanently
follow the telescope position.
Permanently
follow the telescope position.
![]() This button is
active only after you select an object on the chart. If you use
an LX200, the telescope coordinates are reset to those of the
current object. If you use the encoder, the current object is
added to the initialisation list, this also works for initial
alignment.
This button is
active only after you select an object on the chart. If you use
an LX200, the telescope coordinates are reset to those of the
current object. If you use the encoder, the current object is
added to the initialisation list, this also works for initial
alignment.
![]() This button is
active only if your telescope accepts the seek order and if you
select an object on the chart. This moves the telescope to the
selected object.
This button is
active only if your telescope accepts the seek order and if you
select an object on the chart. This moves the telescope to the
selected object.
The right mouse click offers one more option: "Goto Cursor
Position" which you can use to move the telescope to any location
even if there is no object there.
- The cursor coordinates are displayed at bottom-left corner of the screen
- Shift + Move: Continuously identify the objects in the pointer.
- Simple click: Identification of an object and its distance from the previous pointed object
- Alt + simple click: Swap the default identification function (popup or status bar)
- Shift + simple click: Identification of the objects in the circular pointer.
- Shift + Move: Move the chart, same as middle button.(*)
- Click + movement: Definition of the zoom window.
- Click + movement in the zoom window: Move the zoom window.
- Simple click in the zoom window: Zoom
- Ctrl + simple click: Mark objects position on the picture
- Simple click: Display a menu with following functions:
-
- The sky chart is centered where the cursor is located.
- Identify the objects near the cursor position.
- Place a finder circle at cursor position. You can move the circle and then use the left button to fix it.
- Remove the last entered finder circle.
- Remove all finder circles.
- Add a free label.
- Remove the last label.
- Remove all labels.
- Identify the planet, comet or asteroid to follow during animation.
- Sync and Goto telescope command.
![]() Middle
button:
Middle
button:
- Click + movement: Move the current window (*).
- Ctrl + vertical movement: Zoom (*).
![]() Mouse
wheel:
Mouse
wheel:
- Click + movement: Move the current window (*).
- Rotate: Zoom (*).
(*): This functions require a recent processor (>1000Mhz) to work well.
Keyboard shortcut:
| 1 | 10 minutes field of view |
| 2 | 1 degree field of view |
| 3 | 5 degree field of view |
| 4 | 15 degree field of view |
| 5 | 30 degree field of view |
| 6 | 50 degree field of view |
| 7 | 90 degree field of view |
| 8 | 120 degree field of view |
| 9 | 200 degree field of view |
| a | |
| c | |
| e | Show East horizon |
| f | |
| h | |
| l | |
| m | |
| n | Show North horizon |
| p | |
| q | |
| r | |
| R | |
| s | Show South horizon |
| t | |
| w | Show West horizon |
| z | Show the zenith |
| + | |
| - | |
| Keyboard arrow | move the chart to the corresponding direction. |
| Enter: | Hide or show the tool-bars. |
| Space or Esc | Hide or show the main menu. |
| Shift | Slow down the zooming and movement |
| Ctrl | Speed up the zooming and movement |
Command line parameters:
Ciel.exe command will accept the following parameters:
(always use a space between the parameters and their value)
| -ar hh.hhhh | Initial right ascension in decimal hour |
| -de dd.ddd | Initial declination in decimal degree |
| -w dd.dd | Field of view in decimal degree |
| -c nnn.cdc | Load the saved chart nnn.cdc |
| -f "CAT: catid ID: nnn" |
Find object nnn in catalog catid then center the chart at this position Don't use along with -ar or -de |
| -o "LAT:+00d00m00.0s LON:+00d00m00.0s ALT:000m OBS: nom obs" |
Set the observatory location |
| -d yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss | Set date and time |
| -dss "CDdrive ImagePath ImageName reuse" |
Extract a RealSky image corresponding to the initial
chart Set reuse to 1 to use an existing image file instead of reextracting the image. |
| -i | Run iconized. |
| -t | Trace the execution to the file trace.txt |
| -p 1 |
Write a file ciel.pos containing the position of the currently
selected object. |
DDE Interface:
It is possible to obtain information about the current chart or to give command to the program using a DDE interface.
Run ciel.exe then insert the following field in a MS Word
document:
{DDEAUTO ciel DdeSkyChart DdeData}
The field is replaced by the value from the current chart and
is automaticaly updated as the chart changes.
The values returned by line:
line 1: Data update time
line 2: Chart center coordinates and field of vision
line 3: Status bar value, last object identification
line 4: Time of the chart
line 5: Observing place
Example:
27.11.1999 12:06:07
RA: 0h42m42.00s DEC:+41°16'00.0" FOV:+78°00'00"
0h42m44.40s +41°16'08.0" Gx PGC 2557 NGC 224
.SAS3.. D:190.5/61.7' mB: 4.36 b-v:0.92 mB/'2:14.37 RV: -121
1999-11-27T12:05:09
LAT:+46d13m00sLON:-06d09m00s ALT:375m OBS:Geneve
Use DDE Poke function to send command to the program. Only one
command can be sent at a time.
The following commands are available:
| MOVE | RA: 00h00m00.00s
DEC:+00°00'00.0" FOV:+00°00'00" |
chart center and field of vision |
| FIND | CAT: catid ID: nnnn | search an object |
| DATE | yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss | observation date |
| OBSL | LAT:+00d00m00.0s
LON:+00d00m00.0s ALT:000mOBS: nom obs. |
observation location |
| PDSS | CDdrive ImagePath ImageName reuse | DSS cdrom parameters |
| SBMP | ImageName | save as.bmp |
| SGIF | ImageName | save as .gif |
| SJPG | ImageName Quality (0..100) | save as .jpg |
| IDXY | X: pixelx Y: pixely | identify object at position pixelx pixely |
| GOXY | X: pixelx Y: pixely | set the chart center at position pixelx pixely |
| ZOM+ | zoom in | |
| ZOM- | zoom out | |
| STA+ | more stars | |
| STA- | less stars | |
| NEB+ | more nebulae | |
| NEB- | less nebulae | |
| GREQ | switch equatorial grid | |
| GRAZ | switch azimuthal grid | |
| GRNM | switch grid values | |
| CONL | switch constellation shape | |
| CONB | switch constellation boundaries | |
| EQAZ | switch equatorial - azimutal projection | |
| LOAD | .cdc file name | Load the saved chart |
| SAVE | .cdc file name | Save the current chart |
If you are interested in using this function from a program, I
suggest you download an example with Delphi source code from the
source code
page.
It is the responsibility of the calling program to send coherent
values, otherwise results may be unpredictable.