What's to see in the night sky in February?
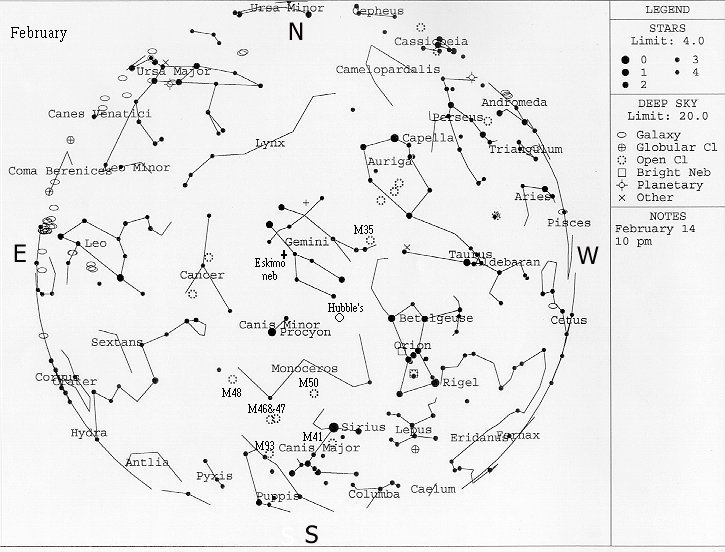
This chart represents the sky as it looks at around 10 PM local
time. Some adjustment should be made for longitude, but it shouldn't be much. Right click on
the chart, select "Save As" and save the image. You can then print
this chart from a photo application, like Print Shop Pro, hold it in front of you with the
direction you are facing at the bottom. Then, raise it above your head and you should be
able to find your way around from there.
Moon phases
New-2/12_____1st Quarter-2/21_____Full-2/28_____
Last Quarter-2/4
Planets
Mercury,
Venus,
Mars,
Saturn and
Jupiter
Mercury rises in the east-southeast around 6:00 am by mid month.
You may just catch it in binoculars before twilight starts. Mercury reaches greatest
elongation on Feb. 21.
Forget Venus this month. It's too close to the Sun.
Mars hangs in the western sky for the month, but is so far
away, (180 million miles or so), that it's hardly worth the trouble. It's in the constellation
Pisces though, so it should be about the brightest thing around and therefore easy to find.
Jupiter stays pretty close to straight up after sunset and is
the third brightest object in the sky, after the Sun and Moon of course. Not a tough target.
Watch the moons go around it during the month. It's fun!
Saturn Is placed such that it defines the Hyades cluster even
more dramatically. You have Aldeberan on the east side of the "V" and Saturn on the west side
of the "V". Makes it pretty easy to find. Crank up the power, if the seeing holds!
Meteor showers
Alpha Centaurids peak-2/8. Watch for a few meteors from the south, early
in the morning.
Delta Leonids peak-2/25. From the east side of Leo.
Deep Sky Objects (DSO's)
Messier Objects M35-Fine open cluster in Gemini, M50-Open cluster
in Monoceros, M46, M47-two open clusters in Puppis, M48-Open cluster in Hydra, M93-Open
cluster in Puppis, M41 in Canis Major
Named DSO's The Eskimo Nebula, (requires 6" telescope minimum),
planetary nebula in Gemini. Hubble's Variable Nebula-Comet shaped nebula in Monoceros.
Monoceros is surrounded by Orion, Canis Major and Canis Minor. The nebula requires a telescope.
It's called "variable" because the gases involved change shape over a relatively short period
of time-like 2 months. Here is a
couple frame gif animation of the motion by a friend of mine here in Tempe.
Here's the link to SEDS as promised.
| January's page | February's page | March's's page | April's page | May's page | June's page |
| July's page | August's page | September's page | October's page | November's page | December's page |

